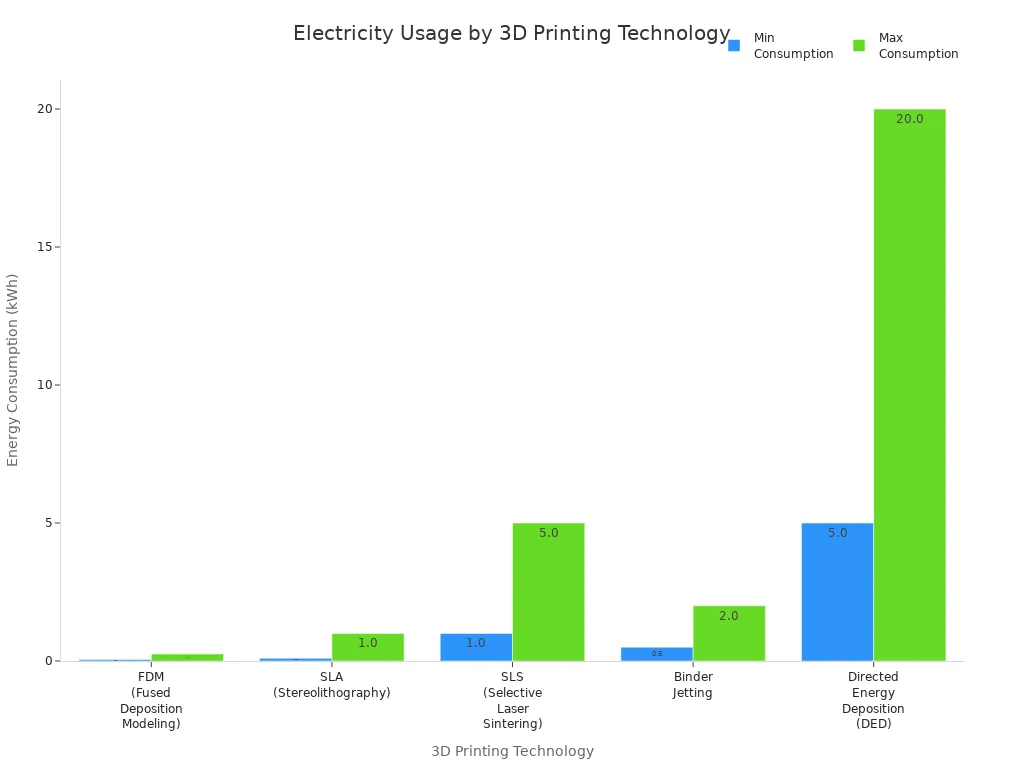
A normal 3d printer uses between 50 and 150 watts when working. Running a 3d printer costs about 2 cents each hour in the U.S. This price is based on average electricity rates. How much energy you use depends on things like heated beds and nozzle temperature. It also depends on how long you print. For example, a printer with a hot end at 401°F and a heated bed at 140°F will use about 70 watts. The chart below shows how different 3d printing technologies use electricity:
|
Technology |
Energy Consumption Range (kWh) |
|---|---|
|
FDM |
0.05 - 0.25 |
|
SLA |
0.1 - 1.0 |
|
SLS |
1.0 - 5.0 |
|
Binder Jetting |
0.5 - 2.0 |
|
DED |
5.0 - 20.0 |
Heating parts, print speed, and infill density change how much electricity your 3d printer uses.
Data and math come from recent studies and U.S. energy prices.
how much electricity does a 3d printer use
Average Wattage
To find out how much electricity does a 3d printer use, you should check the wattage. Most home 3d printers use between 50 and 150 watts when printing. Some bigger desktop printers can use up to 500 watts, but this is not common for home use. Industrial 3d printers use much more energy, usually between 1,500 and 3,000 watts. These machines run longer and have stronger heating parts, so their 3d print power consumption is higher.
The 3d printing power consumption changes with the printer type and your settings. For example, a resin printer made to save electricity might use only 180 watts. If you print for 20 hours in a month, your 3d printer electricity cost will only be a few dollars. The real 3d printer electricity usage depends on things like heated bed temperature, nozzle heat, and how long you print. You can lower your 3d printer electricity by changing print speed, infill density, or layer thickness.
Tip: Industrial printers use a lot more electricity than home printers. If you use a desktop 3d printer, your energy use will be much lower than big commercial machines.
Cost Per Hour
You might ask how much electricity does a 3d printer use in money. The answer depends on your local electricity price and your printer's power use. In the U.S., the average electricity price is about $0.09 per kWh. If your 3d printer uses 100 watts, printing for one hour costs about $0.009. Even if you print for many hours, the electricity cost stays low.
Here is a table with cost examples for different 3d printers:
|
Cost Component |
MK3S (USD) |
MINI (USD) |
SL1 (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Material |
0.15 |
0.15 |
0.60 |
|
Labor |
0.80 |
0.80 |
1.60 |
|
Printer Operation |
0.27 |
0.12 |
0.65 |
|
Margin (30% material) |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.18 |
|
Total (small print) |
1.27 |
1.12 |
3.03 |
For a big print that takes over 40 hours, the electricity cost is still small. Most of your cost comes from materials and labor, not electricity consumption.

When you figure out how much electricity does a 3d printer use, you should also think about your local electricity price. If your price is higher than the U.S. average, your 3d printer electricity usage will cost more. For example, printing 0.3 kg of filament with 0.5 kWh/kg at $0.12 per kWh will cost about $0.018 in electricity. Longer prints and higher heat make 3d print power consumption go up, but the total electricity cost is still low for most home users.
3d printing power consumption depends on:
- Printer model and type
- Print settings (layer thickness, infill density, speed)
- Material choice and needed temperatures
- How often and how long you print
- Note: You can save on 3d printer electricity usage by using features like sleep mode, auto shutdown, and smart power controls.
- If you want to know how much electricity does a 3d printer use for your setup, check your printer's wattage and multiply by your local electricity price. You will see that 3d printer electricity cost is usually a small part of your total 3d printing costs.
References:
- Data on wattage and cost calculations sourced from recent industry studies and U.S. energy statistics.
- Cost breakdown and chart adapted from published 3d printing cost analyses.
- Energy consumption details based on technical documentation and expert reviews.
how much power does a 3d printer use
Power Supply Ratings
A 3d printer has a power supply rating. This number shows the most electricity it can use. For example, a desktop 3d printer may say 360 watts. This means it can handle heavy work, like heating up fast. But when printing, it uses much less power. Most home printers use about 110 to 120 watts. The rating gives extra safety, so the printer works well. Most of the time, it uses less energy. This helps the printer last longer. It also keeps your electricity costs low. Remember, the rating is not the same as real power use.
Standby vs. Printing
You might wonder about power use when not printing. In standby mode, the printer still uses some electricity. It usually uses 3 to 8 watts. This keeps the control board and screen on. The cost for standby is less than $0.01 each day. This does not add much to your bill.
When you print, power use goes up. Most home printers use 80 to 120 watts. Some bigger printers can use up to 300 watts. But this is not common at home. The heated bed uses the most electricity. Resin printers use less energy than FDM printers. If you print for four hours, it costs about $0.06. The table below shows power use for standby and printing:
|
Mode |
Typical Power Consumption (Watts) |
Cost Implication |
|---|---|---|
|
Standby Mode |
3 - 8 |
Less than $0.01 per day |
|
Active Printing |
50 - 300 (commonly 80 - 120) |
$0.008 - $0.05 per hour |
Printing uses much more power than standby. To save electricity, turn off your printer when done. This helps lower energy use and keeps things efficient.
Tip: The heated bed uses the most power. Lowering its temperature or turning it off saves electricity.
References: 1. Technical documentation and industry studies on 3d printing power consumption and energy consumption. 2. Cost and power usage data based on recent expert reviews and published analyses.
3d printer electricity usage factors

Printer Type
- The kind of 3d printer you pick changes how much electricity it uses. Each technology uses energy in its own way:
- FDM printers melt plastic with heated nozzles and beds. They use the least energy of all common 3d printers. Most power goes to the heaters and motors.
- SLA printers use lasers to harden liquid resin. These need more energy because of the laser and extra steps after printing.
- SLS printers use strong lasers to melt powder. They use the most energy. The laser and setup need a lot of electricity.
- FDM printers save more energy and cost less to run. SLA and SLS printers use more power but can make more detailed parts. Pick your printer based on what you need and how much you want to pay for energy.
Heated Bed and Nozzle
Heated beds and nozzles use the most energy in 3d printing. How hot you set them and how long they stay hot changes your electricity use. For example, heating a nozzle to 220°C for ABS uses about 28 watts. The heated bed needs 70 to 120 watts to keep prints stuck. The printer keeps these parts hot while printing, so longer prints use more energy.
|
Component |
Power Consumption (Watts) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Heated Bed |
70-120 |
Keeps the print surface warm |
|
Hot End (Nozzle) |
28-50 |
Melts the filament for printing |
|
Stepper Motors |
~15 each |
Moves the printer parts |
|
Fans |
2-5 |
Cools the print and electronics |
|
Mainboard |
5-10 |
Controls the printer |
|
Display |
1-2 |
Shows printer status |
If you use higher temperatures or bigger beds, you will use more energy. Lowering the bed or nozzle heat can help you save electricity.
Print Duration
How long you print affects your total electricity use. If your printer uses 0.1 kWh per hour and you print for 5 hours, you use 0.5 kWh. At $0.12 per kWh, this costs about $0.06. Longer prints mean more hours of heating and moving parts, so energy use goes up. You can change settings like layer height or infill to print faster and use less power. Shorter print times help you save energy.
Other Factors
Other things can change how much electricity your 3d printer uses:
- Room temperature matters. Printing in a warm room or using an enclosure helps keep heat in, so the printer uses less energy.
- The season can change energy use. Cold rooms make the printer work harder to keep the bed and nozzle hot.
- Printer size and bed size matter too. Bigger printers and beds need more power.
- Using recycled filament can save energy. Making recycled ABS filament uses about 54% less energy than new ABS.
- Upgrading to better power supplies or fans can help you use less electricity.
- Changing print temperature and using smart slicer settings can also lower energy use.
Tip: Printing many objects at once or grouping prints can help you use less electricity.
3d printing makes less waste than old ways of making things, but you still need to watch your energy use for cost and the environment.
References:
1. Technical data on printer types and energy consumption from recent industry studies.
2. Power consumption breakdown adapted from published 3d printing analyses.
3. Print duration and cost calculations based on U.S. energy rates and expert reviews.
4. Environmental and material impact data from 2023 research on recycled filaments and additive manufacturing.
5. Seasonal and ambient temperature effects sourced from technical documentation and user guides.
estimate your 3d printer electricity usage
Using Specs and Math
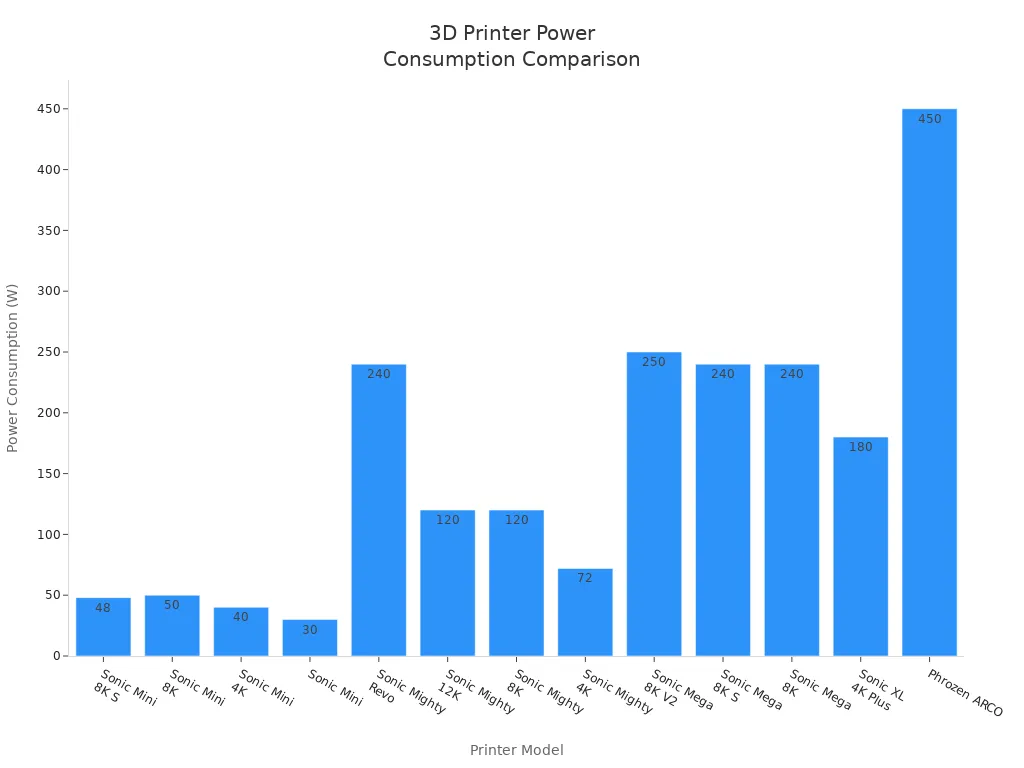
You can figure out how much electricity your printer uses by doing some easy steps. First, look at your printer's manual or label to find its power use. This number is called wattage. It tells you how much electricity your printer needs when printing. Some printers only use 30 watts. Others can use up to 450 watts.
Here is a table with the power use for some popular printers:
|
Printer Model |
Estimated Power Consumption (W) |
|---|---|
|
Sonic Mini 8K S |
48 |
|
Sonic Mini 8K |
50 |
|
Sonic Mini 4K |
40 |
|
Sonic Mini |
30 |
|
Sonic Mighty Revo |
240 |
|
Sonic Mighty 12K |
120 |
|
Sonic Mighty 8K |
120 |
|
Sonic Mighty 4K |
72 |
|
Sonic Mega 8K V2 |
250 |
|
Sonic Mega 8K S |
240 |
|
Sonic Mega 8K |
240 |
|
Sonic XL 4K Plus |
180 |
|
Phrozen ARCO |
450
|
To find out your electricity cost, use this math formula:
Cost = Power (watts) × Time (hours) × Energy Price ($/kWh) ÷ 1000
For example, if your printer uses 100 watts and you print for 5 hours, and your energy price is $0.12 per kWh, you do this:
Cost = 100 × 5 × 0.12 ÷ 1000 = $0.06
You can also use online calculators to help you. These tools let you type in your printer's wattage, how long you print, and your energy price. They show you how much you spend each day, month, or year. If you want to know the heater cartridge wattage, you can use a multimeter to check resistance. Then use a calculator to find the power. This helps you see how much electricity the heating parts use.
Here are the steps to estimate your electricity use:
- Look up your printer's wattage in the manual or tech sheet.
- Decide how many hours you will print.
- Find out your local electricity price.
- Use the formula or an online calculator.
- Change for things like heated bed temperature or print speed to get a better guess.
- Tip: If you use more filament or higher heat, you will use more electricity. Always check your settings before a long print.
Power Meter Method
If you want to know the exact amount, use a power meter. This tool shows you real-time electricity use while printing. Plug your printer into the meter. It will show you how much power you use.
Here is how to check your electricity use with a power meter:
- Plug your printer into the power meter.
- Start a print and watch the meter show the wattage.
- If you want, use the formula P = V × I (Power = Voltage × Current) to check the numbers.
- Write down the total energy used during the print.
- Multiply the kilowatt-hours by your energy price to get the cost.
- Power meters help you see how much electricity each print uses. You can try different settings and materials to see what saves the most energy. If you see high electricity use, try lowering the heated bed temperature or printing for less time.
- Note: Power meters are simple to use and give you real numbers. This helps you make your 3d printing better and save money.
- You can use both ways-specs and math or a power meter-to find out your electricity use. This helps you control your printing costs and make smart choices to save energy.
References:
- Manufacturer technical sheets and product manuals for wattage data.
- Industry guides on electricity usage estimation and cost calculation formulas.
- Online calculator tools for 3d printing energy cost estimation.
- Technical documentation on power meter usage and measurement methods.
- Data and chart adapted from recent studies on 3d printing energy consumption.
electricity usage comparison
3d Printer vs. Household Devices
You may wonder how much electricity a 3D printer uses compared to other things at home. If you check the numbers, you will see that printing does not use much more power than a laptop or a fridge. The table below shows how much electricity some common devices use:
|
Device |
Power Consumption (kWh) |
|---|---|
|
3D Printer |
0.06 - 0.25 |
|
Laptop |
0.06 |
|
Refrigerator |
0.10 |
|
Game Console |
0.12 |
|
Computer Monitor |
0.25 |
A basic 3D printer uses about the same electricity as a laptop when printing. If you use a fancy model, it uses more power, but it is still close to what a computer monitor or game console uses. You can see this in the chart below:

You do not need to worry about your 3D printer making your home use a lot more electricity. Most 3D printers work well and do not use too much power compared to other electronics.
Impact on Electric Bill
When you start printing, you might think your electric bill will go up a lot. But the change is small. If you print for a few hours each week, your electricity use only goes up a little. For example, printing for five hours with a printer that uses 100 watts adds about $0.06 to your bill if your local rate is $0.12 per kWh.
You can keep your costs low by picking good settings and turning off your printer when you are done. Printing with lower heat or for less time helps you save electricity. If you compare the cost of running a 3D printer to other devices, you will see that printing does not make your monthly bill much higher.
Tip: Use a power meter to track how much electricity your printer uses. This helps you make smart choices and keep your costs low.
You can enjoy 3D printing at home without worrying about high electricity bills. The electricity use stays low, and you can control how much energy you spend.
References: 1. Power consumption data for household devices and 3D printers sourced from recent technical studies and energy usage reports. 2. Cost calculations based on average U.S. electricity rates and published analyses. 3. Chart and table adapted from industry research on device electricity usage.
reduce 3d printer electricity usage
Energy-Saving Tips
- You can use less electricity by following some easy tips. These energy-saving ideas help you print more and spend less money.
- Keep the printer door shut between prints. This keeps heat inside and stops the printer from reheating.
- Turn on energy-saving modes. These settings turn off heaters when the printer is not working.
- Switch off extra systems, like the bed vacuum, after printing is done.
- Use the warm air from your printer. Put your printer in a room that needs heat or send the hot air outside to help cool your home.
- Use special ducts or vent hoods to move hot air where you want it.
- Add insulation to the heated bed. Cut a piece of insulation to fit, making holes for screws and springs. This keeps heat in and helps the bed warm up faster, so you use less power.
- Take off the build platform safely before adding insulation. Turn off the printer, unplug it, and remove wires before lifting the bed.
- Make sure the insulation is not thicker than the springs when pressed down, so the printer works right.
Tip: Adding insulation to heated parts and using PWM control on the bed heater can save power, especially for long prints.
Doing regular maintenance also helps save energy. Check for loose screws or worn belts, clean the build plate and extruder, and look at the filament path to stop clogs and overheating.
|
Best Practice |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Use Energy-Efficient Printers |
Pick printers made to use less energy and have better heaters. |
|
Print Multiple Components Simultaneously |
Print more than one part at once to save time and energy. |
|
Regular Maintenance |
Keep your printer in good shape to stop failed prints and wasted power. |
|
Energy Star Certification |
Choose printers with this label for lower energy bills. |
|
ISO 14001 Certification |
Pick printers that help the environment and use less energy. |
Efficient Settings
Changing your print settings can help you use less electricity. You can change a few things to save power and still get good prints.Make the layer height bigger. Thicker layers mean faster prints and less energy, but you might lose some detail.Print faster. Higher speed means less time and lower energy use. Make sure the print still looks good.Change acceleration. Faster acceleration cuts print time but can shake the printer. Find a good balance.Use less infill and smart patterns. Lower infill saves material and energy, but strong patterns keep your print sturdy.Print many parts at once. This fills the bed and uses less energy for each part.Automate post-processing. This saves time and stops energy waste.
Insulate heated parts. Most power goes to the heated bed and extruder. Insulation can cut power use by half.Lower the heated bed temperature. Dropping the bed heat by about 11°C below the glass point can almost cut energy use in half without hurting print quality.
Keep your printer tuned up. Clean nozzles, oil rods, and level the bed to stop failed prints and wasted power.New energy-saving ideas in 3d printing let you change layer thickness, print speed, nozzle heat, and infill. Studies show these changes can cut energy use by up to 72% while keeping prints strong and smooth.Using these settings not only saves you money but also helps the planet. You can print in a way that is good for the earth and still get great results.
References: 1. Technical studies on energy-efficient 3d printing practices and power-saving functions. 2. Industry research on insulation, maintenance, and energy-saving innovations in 3d printing. 3. Recent analyses of printing parameter optimization and carbon emission reductions. 4. Guidelines for energy-efficient certification and environmental management in manufacturing.
Most 3D printers use about 50 to 60 watts when printing. The money you spend on electricity is a small part of your total cost. Print settings, heated beds, and print time all change how much power you use.You can guess your own power use with easy math or a power monitor.Try energy-saving ideas like adding insulation, using lower heat, and turning off the printer when you are done.
If you make smart choices, you can keep your electricity bill low and help the planet.
References:
Technical studies and industry data on 3D printer power consumption and cost analysis.
Guides on energy-saving practices and electricity usage estimation for additive manufacturing.
FAQ
How much electricity does a 3d printer use during a long print?
Most home 3d printers use 0.05 to 0.25 kWh each hour. If you print for 10 hours, you will spend about $0.12 to $0.30 on electricity. The real amount depends on your print settings and how hot the heated bed is.
Tip: Lowering the heated bed temperature helps your 3d printer use less electricity.
What factors influence 3d printing power consumption?
The type of printer, heated bed, nozzle temperature, print time, and room temperature all change how much power you use. These things can make your 3d printer use more or less energy.
Print speed and infill density also change how much electricity you use.
Is 3d printer electricity cost higher than other devices?
Using a 3d printer does not make your electric bill much higher. 3d printers use about the same power as a laptop or a small fridge. Most people pay less than $1 each month for home 3d printing.
|
Device |
Power Usage (kWh/hr) |
|---|---|
|
3d printer |
0.06 - 0.25 |
|
Laptop |
0.06 |
|
Refrigerator |
0.10 |
How can you make your 3d printer more energy-efficient?
You can save energy by using insulated heated beds, lower print temperatures, and power-saving features. Printing many parts at once and turning off the printer when done also saves electricity.
Note: Doing regular maintenance helps your printer use less electricity and keeps it working well.
Does standby mode affect 3d printer electricity usage?
When your 3d printer is in standby, it uses 3 to 8 watts. This small amount adds less than $0.01 to your bill each day. Unplug the printer when not in use to stop all power use.
References: 1. Data and calculations based on recent studies of 3d printing energy consumption and electricity usage. 2. Technical documentation on power consumption and energy-efficient practices in 3d printing. 3. Cost analysis and device comparison from published energy reports.




